There are two different meanings behind the term “brownfield project”. You might be familiar with the term from large building renovations or have seen it associated with environmental movements.
The more well-known meaning comes from the construction and real estate sector and refers to brownfield sites as previously-developed land that is being redeveloped for a new business and can be complicated by pollution or contamination. We want to focus on brownfield projects within the supply chain sector. In the supply chain, a brownfield project reconfigures an existing facility rather than creating a new one on either a greenfield site or a brownfield site. In this post, we’ll look at the pros and cons of brownfield projects in the supply chain sector, as well as some examples.
–> Click here to access the most important factors to consider when selecting a warehouse location
Advantages of Brownfield Projects
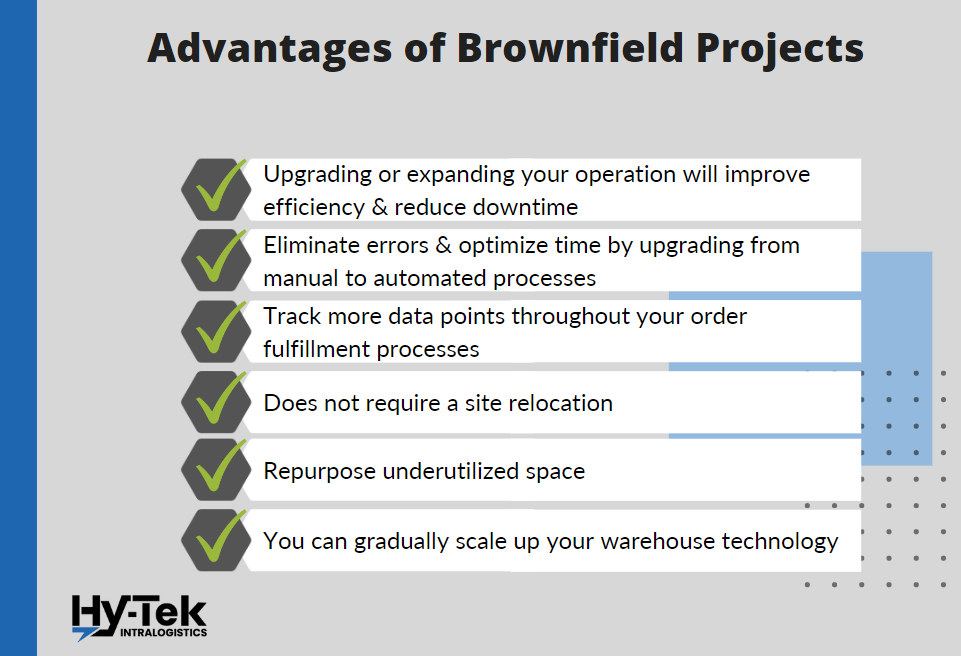
Brownfield projects are desirable because they allow you to transform your current warehouse footprint into something new and improved. The following are some of the advantages.
- Upgrading your systems or increasing your space can improve warehouse performance by increasing efficiency and reducing maintenance downtime.
- Eliminate errors and optimize your time by moving from manual processes to automated processes.
- Increase your data points and track more touch points in your order fulfillment processes.
- It does not require relocation of operations to a new facility which can be costly and disruptive.
- Ability to repurpose underutilized or obsolete space.
- To avoid disrupting your supply chain, you may gradually increase your warehouse technologies and processes to ensure that you’re not introducing too much change at once.
Disadvantages of Brownfield Projects
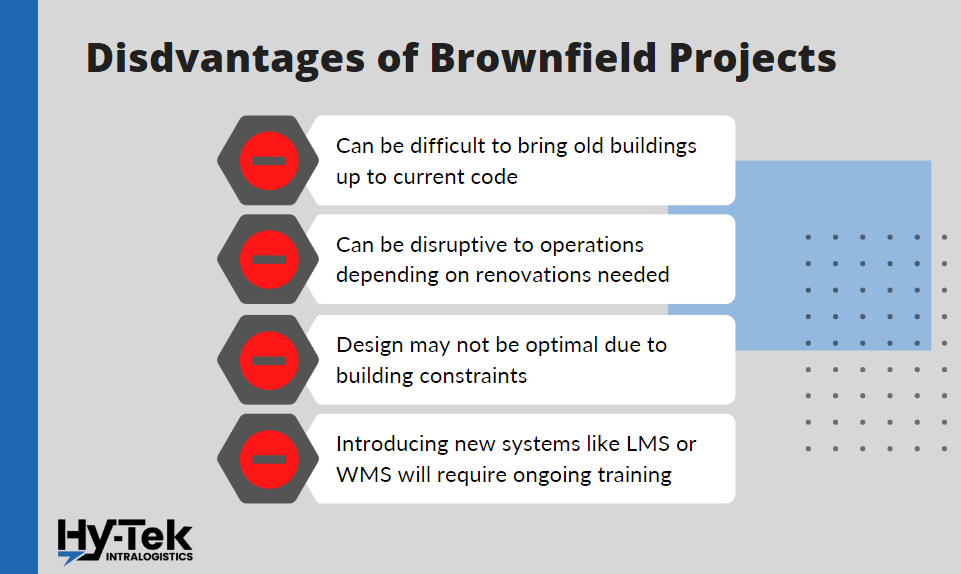
- Old and outdated modules can be challenging to bring up to current code.
- Depending on the required renovations, brownfield projects can disrupt existing operations and might need 1-3 weeks of downtime or weekend cutovers.
- Due to building constraints or configuration, the design may not be optimal compared to a greenfield project.
- Introducing new systems like a Labor Management System or Warehouse Management System will require ongoing training and administrative costs, and upkeep.
Brownfield Project Examples in the Supply Chain Industry
- The current tenant wants to increase storage capacity by expanding their warehouse.
- Upgrading outdated modules (sortation, conveying, and picking solutions) to improve warehouse performance.
- Adding additional dock doors to the current warehouse.
- Upgrading from traditional material handling equipment to autonomous mobile robots.
- Rewiring the current warehouse to support a new warehouse control system and warehouse management system.
- Adding new modules (labeling system, voice picking, vertical lift module) to optimize efficiency and move from traditional systems to digital systems.
Core Differences between Supply Chain Brownfield Projects and Brownfield Construction/Redevelopment Sites
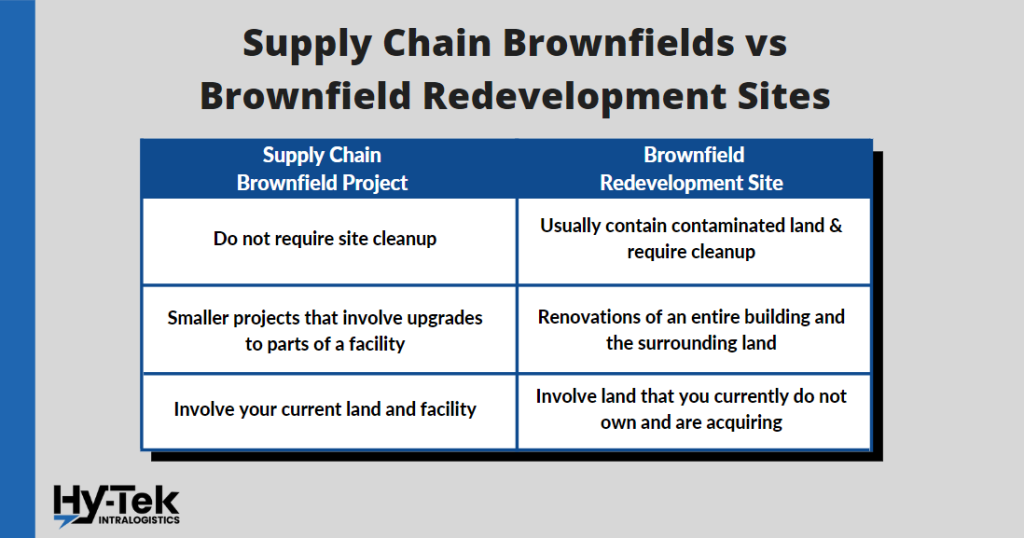
While the names are the exact same, the items involved are very different from each other.
- Brownfield redevelopment sites are more involved because they usually require contaminated land, whereas traditional supply chain brownfield projects do not.
- Brownfield projects can be smaller projects that require an expansion of a storage room or an update to the material handling equipment. Brownfield redevelopment sites are renovations of the entire building and the surrounding land.
- Brownfield projects in the supply chain involve your current land and facility, whereas brownfields in construction involve land you do not currently own and are acquiring.






