Surprisingly, Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) have been around since the 1950s.
Traditionally these AGVs follow along marked lines on the floor or use lasers or radio waves for navigation.
However, current technology allows for workflows to be programmed into robotic lift trucks, allowing for free movement around a warehouse and not requiring expensive warehouse changes when changing the truck’s work process.
While technological advancements breed innovation and excitement, many companies are standing by and waiting for case studies and established long term success to be reported before they throw any cash around.
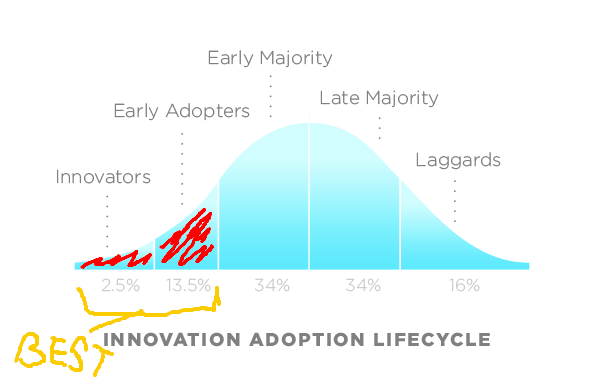
However, in every single industry that technology disrupts it runs a typical course called the technology adoption curve.
The goal is to be on the left side of this graph; you get involved in the process before a majority of competitors and as a result, you reap the rewards of lower operating costs, increased margins, faster production time and lower acquisition costs.
While there are many different kinds of autonomous robots, let’s break down robot forklifts to see if they are right for your warehouse.
Best Applications for Robotic Lift Trucks
| INDUSTRY | APPLICATIONS |
|---|---|
| Automotive | 2-3 Shift Operations |
| Pharmaceutical | Long runs between dock/pallet and rack |
| Manufacturing | Repeatable Paths |
| Food & Beverage | Dirty |
| Aerospace | Dangerous |
| Logistics | |
| Retail |
The Opportunity Savings and Benefits Robotic Forklifts Provide
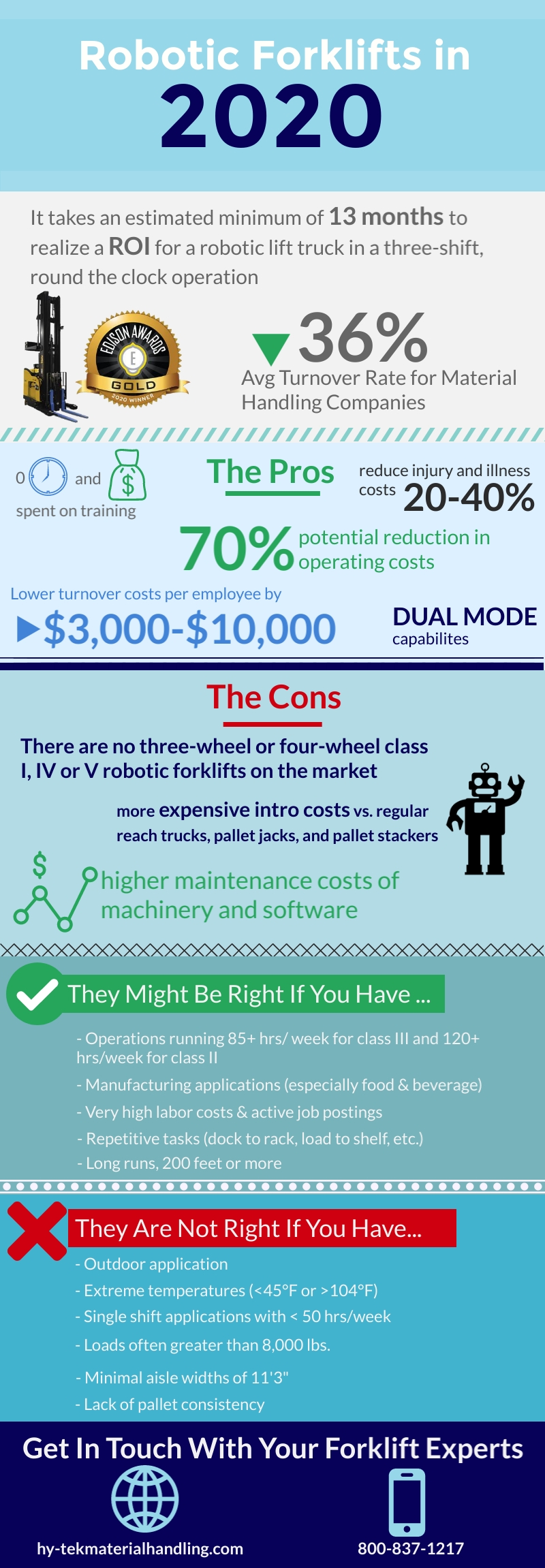
The Bureau of Labor Statistics reports warehouse labor turnover at 36%.
Replacing warehouse workers is a process that involves time for recruitment, interviews, and training.
This takes valuable time away from Operations Managers and Supervisors which means less time available to work on supply chain and management in the warehouse.
Some experts calculate the real costs, when you factor in lost productivity, reduced quality, and efficiency in the early stages of a new associate’s tenure, could be as much as 150% of salary.
These costs are made up of:
- Accidents due to inexperienced operators
- Product located incorrectly (lost inventory = lost sales & lost sales = lost customers)
- HR and Warehouse Managers time to interview, hire and train talent
- Less total hours worked by operators while finding a replacement
- Advertising fees, recruiting fees and screening costs
- Drug testing, background checks, and possible relocation costs
Speak with a robotic forklift expert
In addition to saving on turnover, robotic lift trucks do not require days off for vacations, personal days, lunch breaks or human errors, such as mispicks or lost inventory.
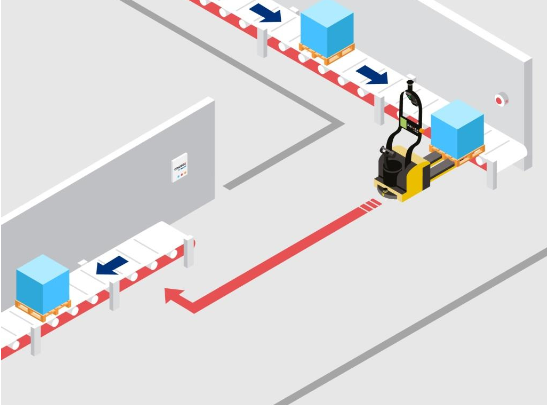
Robotic lift trucks (RLT’s) will pick up the load from the point they’re programmed to and take it to the point that they are told to.
The only human error can occur in programming the lift trucks routes.
How Robotic Lift Trucks Work
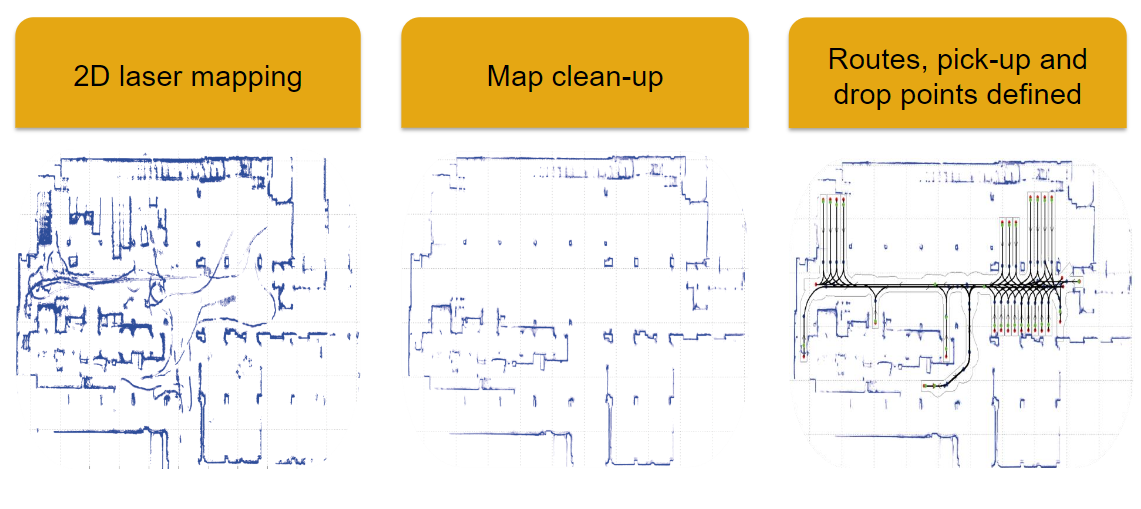
The robotic lift truck uses similar hardware and technology used in self-driving vehicles to turn a standard model into an autonomous vehicle; Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR).
LiDAR is defined as a surveying method that measures the distance to a target by illuminating the target with laser light and measuring the reflected light with a sensor.
Thus, the robotic lift truck compares in real-time, what it sees with the reference map it is programmed to and navigates with accuracy.
Robotic Laser Mapping
The ability of RLT’s to run with zero, partial or full interface with warehouse management systems (WMS) allows for a fast startup with little infrastructure modification, provides tracking of load movement and enables informed management decisions.
Most warehouses aren’t ready to spend seven figures on a fully built and programmed complex RLT application and we get that.
So, in this instance, we suggest you consider scaling your operations.
One option is to begin with one RLT and keep the process simple.
An example of this is an operator unloading a trailer and having an AGV pick up the load and drive it to the rack where another operator will pick the load and put it away.
Later on, you can upgrade this as your application grows and you become more comfortable with how RLT’s coincide with your warehouse.
RLT’s are broken down into two different categories:
- Basic Applications
- Complex Applications
Basic applications require one or two simple tasks, whereas complex applications will ask the lift truck to perform multiple tasks.
Robotic Forklift Basic Applications
Location Scanning
The RLT’s scanning technology enables it to check the availability of locations in a floor storage area.
Using the laser on the front of the truck, the RLT can scan several loading bays, detect free locations and place a load there.
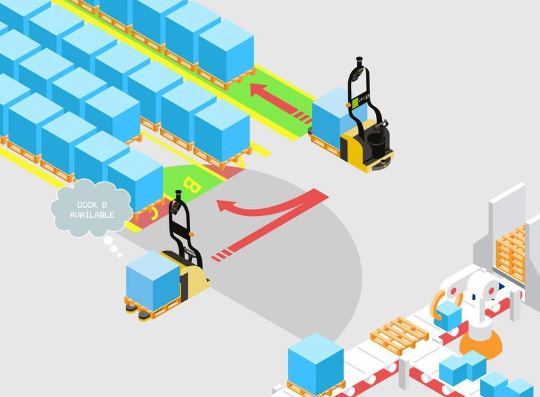
Dock Staging and Put Away
Transports loads to shipping docks from receiving docks to storage.
This process moves loads from docking areas directly to the programmed storage area and returns to grab another load.
Robotic Forklift Complex Applications
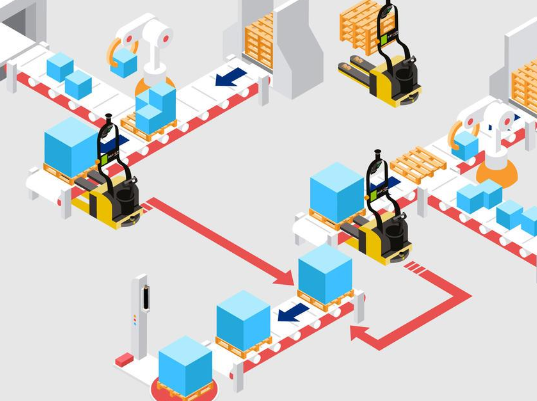
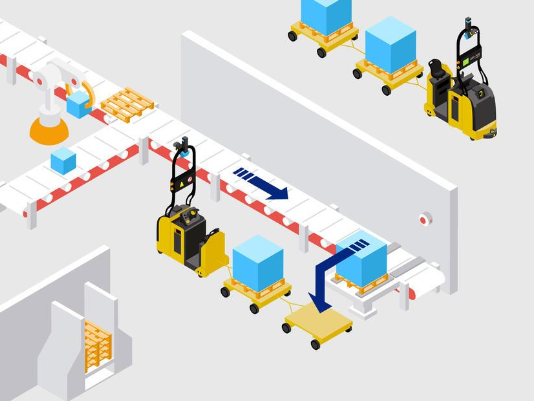
Machine Interfacing
Drop off and pick up loads from production lines, workstations or storage areas.
The robotic lift truck will also transfer materials or goods between production cells.
The last section in this article provides a good breakdown of man and machine interfacing within a warehouse.
Conveyor Interfacing
The RTL will interface with your infrastructure, whether that is smart conveyors, automatic wrapping machines, stacker cranes, robotic palletizer, etc. moving loads from one station to the next.
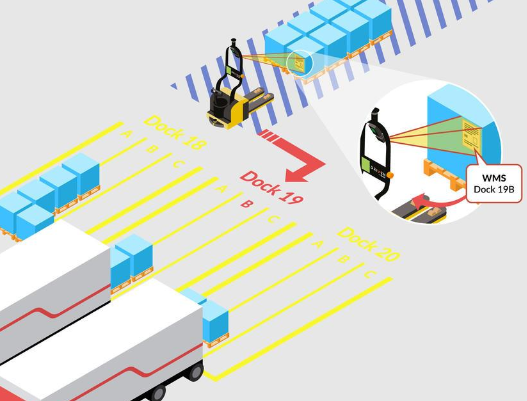
Bar Code Scanning
An optional barcode reader can be added to your robotic lift truck, allowing for products to be tracked through the factory or warehouse.
The barcode reader triggers a transport order as soon as the RTL picks up the pallet to deliver it to the programmed location.
The RTL transmits the load information by interfacing the WMS or ERP.
Logistics Trains
Logistics trains allow transportation of multiple carts hauled by an RLT.
When the operator signals the ERP/WMS, the RLT moves to the station, where the operator retrieves what they need.
Pressing a button on the RLT touch screen sends it to its next destination.
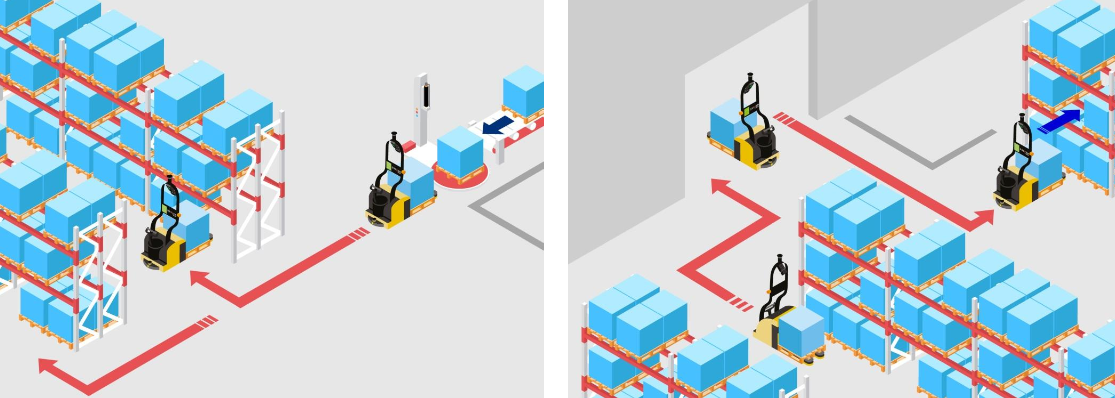
Machine to Storage & Storage to Retrieval
RLT’s enable dependable storage of loads up to 6.56 feet high (in very narrow aisles).
RLT’s can help reduce product damage by controlling speed, acceleration, and controlled stops.
Whether your application is a warehouse, floor or buffer storage the scalable range of RLT’s can help meet application demands while reducing opportunities for accidents caused by operator error or misuse of equipment.
The video below shows what a fully automated process looks like.
FAQ
What are the Advantages of Using Robotic Forklifts?
• lower your turnover costs per employee by $3,000 to $10,000
• 0 time and money spent on training
• reduce injury and illness costs by 20-40%
• the ability to switch to manual mode to accommodate changing operational needs
• handling repetitive, simple transport to free up labor to focus on more engaging tasks
• according to Balyo it is estimated that it takes a minimum of 13 months to realize an ROI for a robotic lift truck in a three-shift, round-the-clock operation
• lower installation costs, navigational infrastructure, and truck costs when compared to AGV and laser-guided trucks
What are the Disadvantages of Using Robotic Forklifts?
• not suitable for one-shift operations
• can handle simple and fairly complex tasks but not suitable for multifunction, complex applications
• more expensive intro costs than regular reach trucks, pallet jacks, and pallet stackers
• no three-wheel or four-wheel class I, IV or V robotic forklifts on the market