If you are looking for a way to optimize your warehouse floor space and increase storage space capacity there are many types of pallet racking to pick from. An excellent place to start for low-cost and low-complexity applications is a conventional pallet racking system. This is the original way to do this, and it is still the quickest to install and most cost-effective solution.
This blog post will discuss the benefits of conventional pallet racking, the disadvantages, and how to tell when you need to change from a conventional setup to a new system.

What is Static Racking?
Static racking is a warehouse storage system that uses shelves or racks to store goods. Pallets are placed on these shelves, and material handling equipment is used to load and unload the rack. This system is prevalent because it is very customizable, is low cost, and can improve the use of space in a warehouse.
Types of Static Rack
- Rolled Form Pallet Racking – The most popular sort of static racking is this one. It’s a medium to heavy-duty rack that can handle a lot while readily customized to your warehouse’s specifications. The racks are made from steel and then painted or hot-dipped in galvanizing for corrosion resistance.
- Structural Pallet Racking – This type is the heavy-duty version of rolled-form racks. They’re made from structural steel I-beams and C-channels and painted or hot-dip galvanized for corrosion resistance. They’re more expensive than rolled-form racks, but they can handle more weight and impact.
- Drive-in Racks – These are used to store pallets more densely. Pallets are stored behind one another, limiting access to each pallet, but creating greater storage density.
Pallet Rack Components
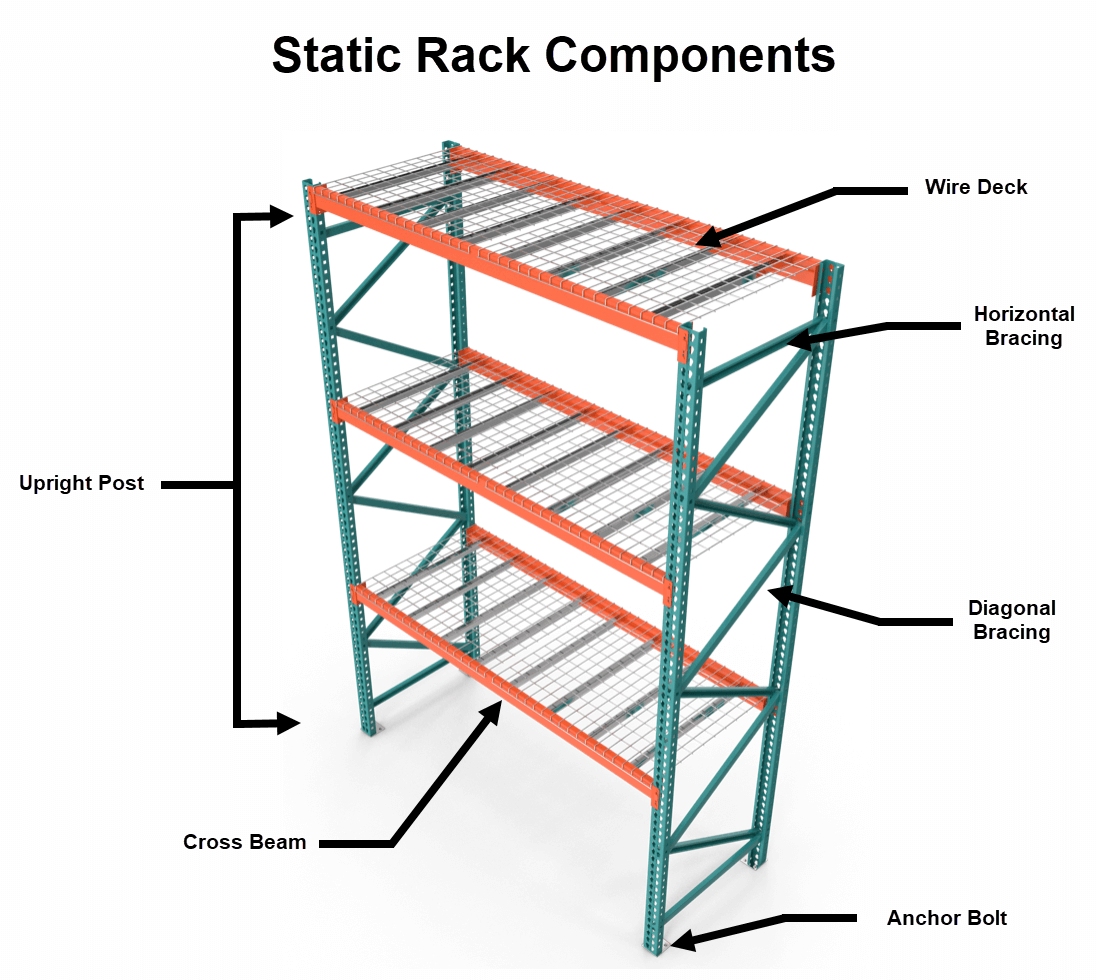
Upright Frames
Upright frames stand vertically and are used as columns to which the beams can connect. The front face of uprights (the bit you can see when looking at the rack) has slots that the beams fit into. Uprights can be single or double slotted.
Cross Beam
These are horizontal load-bearing members that connect the uprights. Beams typically have a step design to fit into the slots of the uprights and come in a wide range of lengths.
Wire Decking
Wire deck sits across the two cross beams and increases the safety and stability of a pallet racking system by reducing the chances of pallets falling or losing materials falling, and allowing non-palletized loads to be stored.
Bracing
The diagonal struts, combined with the square struts, form the frame’s structure. The load-bearing capacity of the posts is enhanced by diagonals that support the top and bottom of the upright posts.
Anchor Bolt
Anchor bolts act just as the name suggests. They anchor your racks to the floor to ensure stability and additional safety.
Standard Rack Sizes and Dimensions
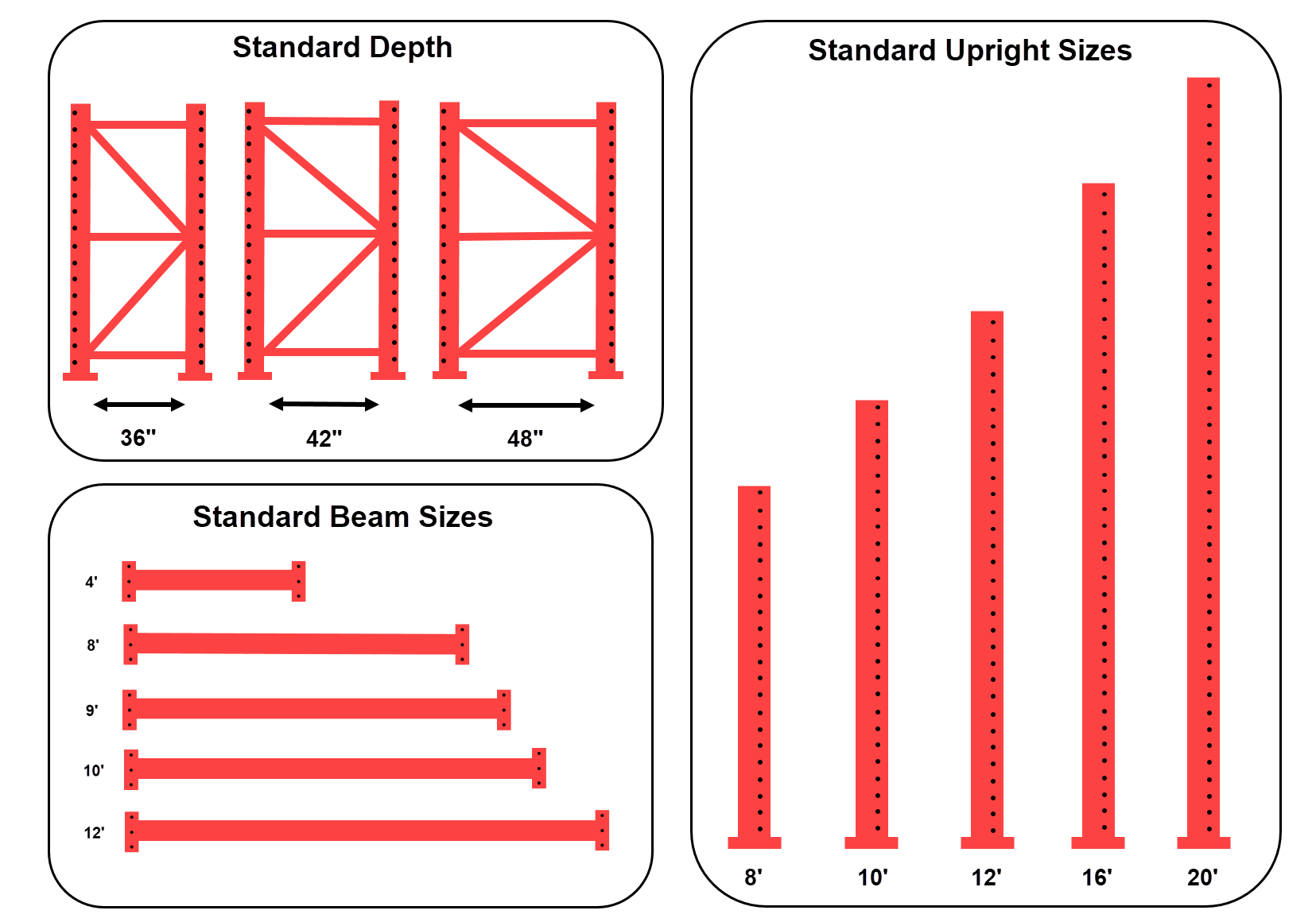
Standard Pallet Rack Beam Sizes
The most frequent pallet rack beam dimensions are 4′, 8′, 9′, 10′, and 12′. Other beam lengths aren’t usually required based on typical pallet sizes.
Standard Pallet Rack Upright Sizes
The typical depth of a pallet rack is 36″, 42″, and 48.” Standard upright heights range from 8′ to 24.’ The most popular upright heights are 8′, 10′, 12′, 16′ and 20′.
Roll-formed Teardrop is the most common design of selective pallet racking. Most companies provide a teardrop rack that is either roll-formed. If your facility was built within the past 15 years, the chances are that you have teardrop selective racks.
How to Determine Weight Capacity
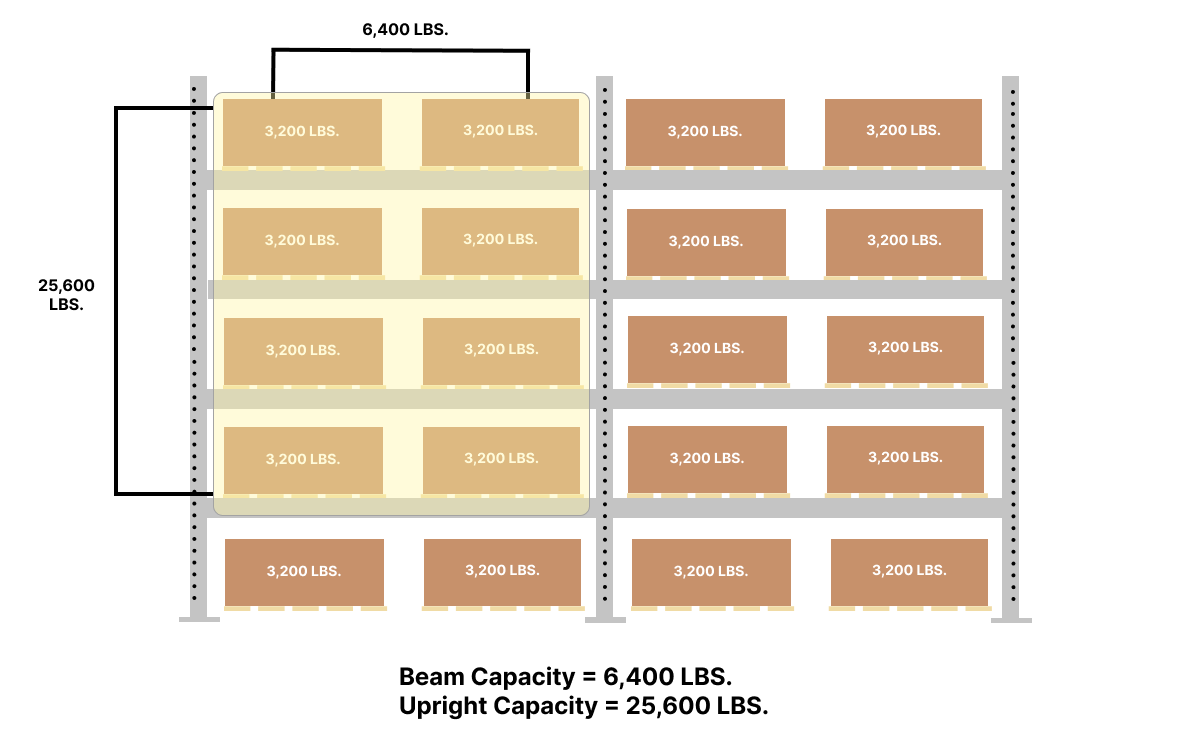
The first step is to determine the maximum weight of the objects you’ll be storing. In most cases, it’s preferable to overestimate rather than underestimate the weight of the loads.
For example, if the maximum weight of your object is 800 pounds and you want to put four on a pallet, the load weight is 3200 pounds. If you want to store two loads per pair of beams, then the rated capacity of your beam pair needs to be 6,400 pounds. To determine the capacity requirement of your upright pair, multiply the beam pair capacity by the number of beam levels. In our example, if you have four beam levels, then your upright capacity will need to be at least 25,600 lbs. Please refer to the image below for a visual of storing inventory.
How to Plan your Layout
To start planning your site, you need to know your available floor space, warehouse height, and any obstructions in the space. Before starting, it is best to contact material handling experts or warehouse contractors for their project suggestions.
1. Understand your Storage Needs
Will you work with oversized, dense pallets or smaller pallets with individual products? How long will your SKUs be stored? Do you need a designated area for freezer and cold storage space? Would mobile systems be more helpful?
Knowing exactly what you will need can help you select and integrate the appropriate static pallet racking solution.
2. Measure Warehouse Area
To guarantee that you make the best use of all the space in your warehouse and avoid ordering racks that are too tall to fit, measure from wall to wall and floor to ceiling. If your warehouse has a slanted roof, measure from both the peak of the ceiling and the ceiling height at the sides of the structure.
3. Select Proper Material Handling Equipment
To capitalize on your storage space, you’ll want your aisles to be as narrow as possible. However, this will be determined by your material handling equipment’s right angel stack capability and matching function with the process.
Other considerations that will determine your equipment are the ceiling height and the distance of your runs.
4. Determine Employee Service Locations
This area will consist of:
- Modular offices
- Restrooms
- Storage rooms
- Equipment charging stations
- Breakrooms and lounges
- Lockers
5. Consider Essential Non-Storage Spaces
When you map out your warehouse, you’ll want to consider shipping and receiving areas, packaging stations, sortation, and even unchangeable factors throughout your warehouse (pillars, support beams, doors, etc.) that will need to be built around.
6. Look at your Racking Options
Once these items are covered, you can determine which static racking system is right for your application – roll form, structural, or drive-in racking. When you decide, you are now ready to begin implementing your strategy.
FAQ
What are the benefits of conventional racking?
There are several benefits of using a conventional racking system in your warehouse. The main benefit is that it allows you to increase storage capacity by taking advantage of vertical space, which means less floor space will be needed for storage, and more room can be used for other purposes like production or administration tasks.
Conventional pallet racking systems are also easy to install and maintain to get up and running quickly and without hassle. And because the shelves are adjustable, you can easily change the configuration to meet your changing needs.
There are several benefits to using a conventional pallet racking system in your warehouse. Some of the most important ones are:
Quick and easy installation: A conventional pallet rack can be installed quickly and easily, with few special tools or equipment.
Quick and easy installation: A conventional pallet rack can be installed quickly and easily, with few special tools or equipment.
Low cost: Conventional pallet racks are some of the most affordable storage solutions on the market.
Modular design: Conventional racks are modular, meaning they can be adapted to fit almost any space.
Wide range of sizes and capacities: There is a wide range of sizes and capacities available for conventional pallet racks, so you can find one that fits your needs perfectly.
What are the disadvantages of static pallet racking?
There are a few downsides to using this system in your warehouse. The first disadvantage is that it requires a lot of floor space and can make things cramped if you don’t have enough room to work with.
Another downside is that conventional pallet racking systems are not very flexible, which means they’re only suitable for specific load sizes.
Another disadvantage is that it requires material handling equipment like forklifts or cranes to move heavy items onto the shelves. If you don’t have these tools available, this system might not be suitable for you.
When should I switch from static pallet racking to dynamic racking?
You may want to consider switching from a conventional pallet racking system if your business has grown and now occupies more than half the floor space in your warehouse, or when there’s an increase in demand for products stored on this type of shelf because customers can easily access them without having any material handling equipment.
If you are looking for greater density, you might consider switching to a dynamic racking system. This system is more expensive than conventional pallet racking, but it can be worth the investment if your business has outgrown its current storage capacity.
Does Pallet Racking Need to be Bolted Down?
In some cases, pallet racking does not need to be bolted down; however, bolting the uprights to the ground is strongly recommended.
Some benefits to bolting the racks down are increased stability and safety. If you choose to bolt down your racks, make sure to use the proper fasteners for the type of rack you have.
How do dynamic racking systems compare to static racking systems?
Dynamic racking systems are more expensive than static racking systems and can offer greater storage density and product access.






